To evaluate whether an invader is a friend or foe, the immune system employs a number of checkpoints. In this process, there are three lines of defence: physical barriers like the skin and mucous membranes, the innate immune system – a group of cells that identify invaders without the help of the adaptive immune system, and finally, the adaptive immune system – a group of cells that fight infection with antibodies.
Continue reading to learn more fun facts about the immune system.
1: The immune system is essential for human survival.

The immune system protects the human body from external infections by providing both natural and acquired protection. Without the immune system, the human body can become infected, which can spread to many organs and organ systems and cause death. Certain malignancies are caused by the body’s immune system malfunctioning.
2: Inflammation and fever are both healthy signals.
Fever and inflammation are uncomfortable, but they’re signals that your body is working properly. Fever causes the release of white blood cells, stimulates metabolism, and inhibits the growth of certain organisms.
Each injured cell releases histamines, which causes inflammation. Cell walls dilate as a result of the histamines. Inflammation manifests itself as redness, heat, pain, and swelling. As a result, your body reduces the irritant’s impact.
3: The immune system is influenced by sunlight in a variety of ways.

Vitamin D is produced naturally by your body when it is exposed to sunlight. This can help prevent a variety of problems, including depression, heart disease, and certain malignancies. It’s even beneficial to those who suffer from autoimmune diseases.
On a bright day, a fair-skinned individual can obtain all the vitamin D they require in about 10 minutes. However, too much sun might harm your immune system in the short term and eventually lead to skin cancer. Remember that while some sun is beneficial, you must protect your skin when spending time outside.
All people should use sunscreen with broad-spectrum UVA and UVB protection, a Sun Protection Factor (SPF) of 30 or greater, and water resistance, according to dermatologists. You should also wear protective gear when the sun is particularly intense, such as sunglasses, long-sleeved shirts, long pants, and wide-brimmed hats. Also, stay largely in the shadow between 10 a.m. and 2 p.m., when the sun’s rays are the strongest.
4: The blood cells are the most significant component of the immune system.
The immune system’s development and function are dependent on blood cells. White blood cells are progenitors to immune cells such leukocytes, lymphocytes, and antibodies, which help the body defend itself against external infections. Immune cells are specialised blood cells that include phagocytes, T-cells, and B-cells, among others. The thymus produces some of them, whereas the spleen and lymph nodes create others.
5: A small percentage of your blood is made up of white blood cells.
Because your immune system is continuously working to protect you from diseases and fight infections that you already have, you may anticipate the system’s troops — white blood cells — to make up a big amount of your blood. This, however, is not true. Only 1% of the cells in an adult’s blood (5 litres) are white blood cells. Besides, there are enough white blood cells to do the job. White blood cells can be found in between 5,000 and 10,000 cells in each microliter of blood.
6: The immune system relies on the appendix.
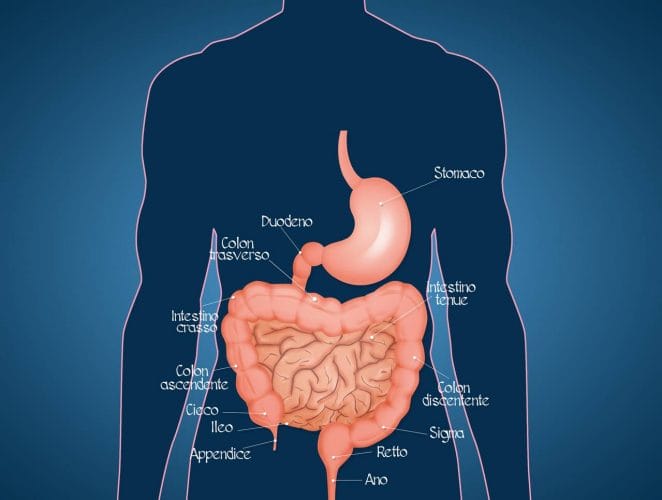
The appendix, which is assumed to be a vestigial organ, may play an immunological role. The appendix has long been considered a vestigial organ that appears to have no use in the human body’s functioning. Recent research, on the other hand, has thrown some light on the appendix’s true purpose. The appendix appears to house immune systems known as Innate lymphoid cells (ILC), which aid in the repopulation of the gut microbiota after an infection or antibiotic treatment.
7: Some people have a weak or non-existent immune system.

SCID, or severe combined immunodeficiency disease, is a hereditary illness that causes the absence of immune cells, making the person vulnerable to external viruses and diseases. Various SCID treatments have been discovered, including bone marrow transplantation from a related individual or a sibling, which aids in the restoration of the immune system in the affected individual.
8: The human body creates a large number of antibodies.
Antibodies are created by the immune system in a variety of ways. Antibodies are immunoglobulins produced by the immune system’s B-cells. Antibodies produced by B cells are different from those produced by T cells. Antibodies are Y-shaped molecules that target pathogenic proteins and markers while also attracting other immune cells to the disease for targeted destruction and eradication.
9: Immunity is mentioned for the first time around two millennia ago.

Although the first vaccine was developed in the late 1800s, humans have long acknowledged the value of immunity. The Greeks discovered that persons who had previously survived smallpox did not get the disease again during the epidemic of Athens in 430 B.C.
According to a 1998 paper in the International Journal of Infectious Diseases, these survivors were frequently called upon to care for people who had smallpox. Chinese medics began blowing dried smallpox scabs into the noses of healthy patients in the 10th century, and the patients contracted a mild version of the disease – and those who survived were resistant to smallpox. In the 1700s, this procedure, known as variolation or inoculation, expanded throughout Europe and New England.
10: Your immune system is harmed by stress.

Your immune system is prepared to deal with everything you throw at it. But it’s only capable of so much. Your immune system is greatly influenced by stress. Cortisol, adrenaline, and other stress hormones are released from the adrenal gland as a result of a series of events during stress. They work together to assist your body deal with stress.
Cortisol is normally beneficial because it reduces inflammation in the body produced by stress-induced immunological responses. Stress hormones, on the other hand, can influence how the body operates over time if a person is continuously stressed. This increases your chances of developing health issues such as depression and anxiety, digestive problems, illness of the heart, sleep disturbances, memory and focus problems.
Sources:Live Science, Bioexplorer





GIPHY App Key not set. Please check settings