Tyrannosaurus Rex is the most well-known dinosaur, having inspired several books, films, television shows, and video games. Tyrannosaurus lived up to its reputation as one of history’s most terrifying creatures. Tyrannosaurus possessed 60 teeth, each measuring up to 20cm (8 inches) long, and its bite was roughly three times stronger than a lion’s. Bite marks discovered on the bones of Triceratops and Edmontosaurus prove that Tyrannosaurus could crunch through bone. The bones of Tyrannosaurus prey were discovered in the faeces of the dinosaur.
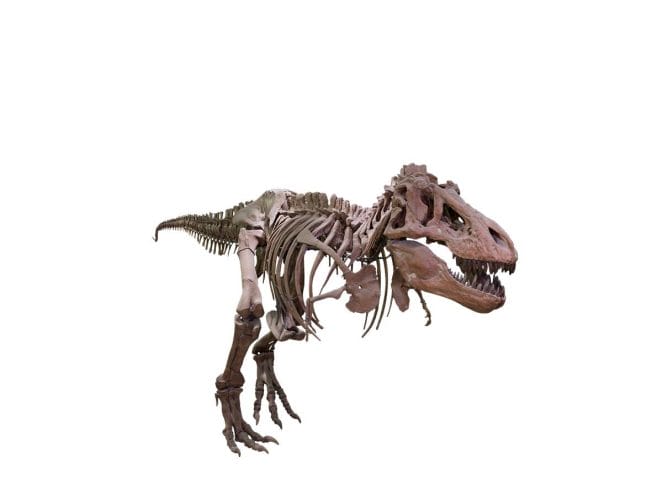

Tyrannosaurus is perhaps one of the most well-known dinosaurs, and it was one of the last major carnivores before the great extinction 66 million years ago. It wasn’t the biggest, but it was one of the most dangerous predators around.
Tyrannosaurus, like other carnivorous dinosaurs in its family, had a huge skull and a long, heavy tail. Its short, two-fingered arms were roughly the length of a human’s and did not even reach the tip of the nose when stretched. Tyrannosaurus Rex could bite through solid bones with its gigantic fangs, which were up to 18 cm long and curled inwards. Tyrannosaurus tooth was lost, but it grew back within a few weeks. Tyrannosaurus’ relatively large weight most likely prevented it from reaching very high speeds. It was still a successful hunter, but scientists believe it ate carrion as well.
Researchers in the US state of Montana unearthed Tyrannosaurus rex bones in 2003. Because a bone was too huge to be transported by helicopter, it had to be sawn through. The scientists who later investigated the bone were shocked to find traces of blood arteries that had not fully petrified inside the million-year-old fossil. In 2007, researchers led by Mary Schweitzer of North Carolina State University studied the discovery and discovered soft tissue and blood arteries intact within the femur. They were able to isolate the protein collagen, which is an organic component of skin, tendons, and bones, as a result of this.
In 2008, Harvard University in Cambridge researcher Chris Organ and his team discovered that Tyrannosaurus was more closely linked to birds than to other animals. Some amino acid chains, the building blocks of the “primordial protein,” may also be identified. When compared to modern species’ amino acid chains, the sequences of tyrannosaurus most closely resemble those of chicken, newt, and frog. The parallels to chickens, in particular, support the theory that dinosaurs and modern birds are linked.
The following are some of our favourite interesting facts about Tyrannosaurus Rex, which will provide you with the most comprehensive understanding of T-Rex possible, which you can then share with your friends.
1: Tyrannosaurus Rex quick facts:
Name: Tyrannosaurus (Greek for “tyrant lizard”); pronounced tie-RAN-oh-sore-us
When it lived: Late Cretaceous, 90-66 million years ago
Type of dinosaur: Large Theropod
Location: USA, Canada
Habitat: High humidity and semi-tropical temperatures of western North America.
Length/Weight: 12 meters/7000kg
Diet: Carnivorous
Distinguishing Characteristics: Large head with forward-facing eyes, massive muscular jaws, robust serrated teeth, a powerful tail, and tiny arms.
Named by: Osborn (1905)
2: Why is T. rex the king of dinosaurs?
Tyrannosaurus rex (“king of the tyrannical lizards”), commonly known as “The King of the Dinosaurs,” was a gigantic carnivorous theropod dinosaur that lived between 90 and 66 million years ago. Tyrannosaurus Rex is the most well-known dinosaur. This is largely due to the fact that it was the first enormous carnivorous dinosaur to be discovered, and it was long thought to be the largest ever.

Another factor was that it was most likely the world’s most ferocious meat eater. It was enormous, standing over 40 feet tall with the most strongest head of any dinosaur. It also had the largest teeth of any dinosaur, teeth that were both sharp and cutting edged, as well as massive and robust, capable of crushing bones.
3: When was T. rex discovered?
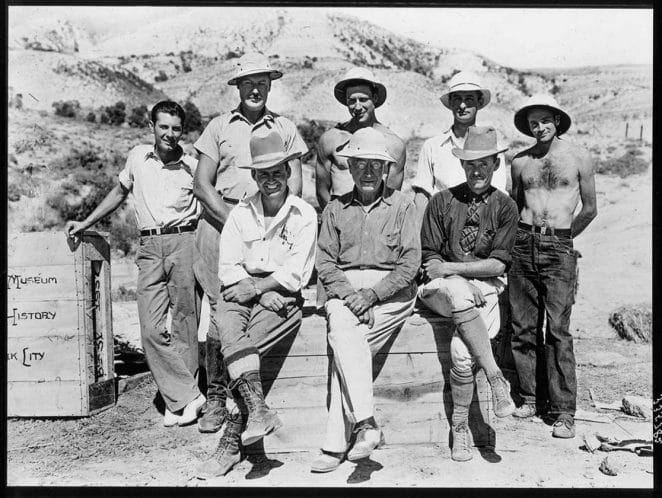

In 1902, Barnum Brown, an assistant curator at the American Museum of Natural History, found the holotype specimen of T. rex in Montana’s Hell Creek Formation. The holotype is the only example of a new species that is used to give it a name. In the following years, he and his colleagues would uncover numerous more species in the West. Henry Fairfield Osborn, then-museum president, named the dinosaur Tyrannosaurus rex in 1905.
4: How big was T. rex?
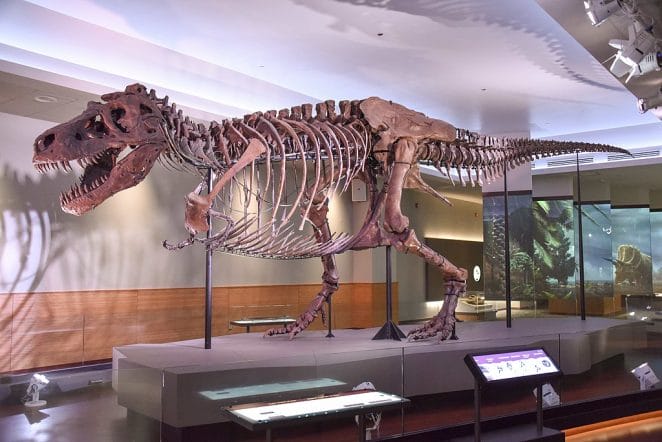
Scientists estimate that a Tyrannosaurus rex might have been up to 40 feet long and 12 feet tall based on fossil specimens.
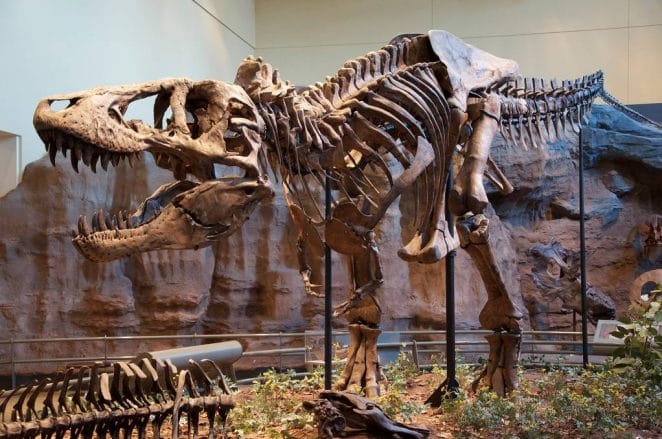

With skin and flesh on its massive bones, T. rex was estimated to weigh between 11,000 and 15,500 pounds (5,000 and 7,000 kg). This is around the same as the largest African elephant.
5: How fast was T. rex?
Dinosaur speeds are typically estimated using fossil trackways. Based on the best-preserved trackways, the most reasonable interpretations suggest a walking speed of 3 to 6 miles per hour. Biomechanics is frequently used to determine running speeds. Researchers look at the muscles and body designs of large living creatures, as well as the stress that running puts on the body.
Scientists believe T. rex was a slow runner, clocking in at around 10 miles (16 kilometres) per hour, or about the same as a typical human runner. According to these experts, T. rex’s size slowed him down. Bones, muscles, and posture all contribute to this.
6: What did T. rex eat?
Teeth are the strongest indicators to dinosaur nutrition, aside from fossilised stomach contents. Carnivorous animals’ teeth are typically sharp, serrated blades that resemble daggers. These teeth aid the animal in both killing and slicing its prey before consuming it. Tyrannosaurus rex ate big chunks of meat rather of chopping or grinding it. T. rex possessed a hinge in the middle of its lower jaw that may have helped absorb some of the shock caused by fighting prey.
7: Where did Tyrannosaurus rex live?
The majority of T. rex fossils have been discovered in the Northwest, in places like Montana and South Dakota. In Alberta, Canada, T. rex fossils have also been discovered.
8: When did T. rex live?
T.rex lived between 90 and 66 million years ago, at the conclusion of the Late Cretaceous period.
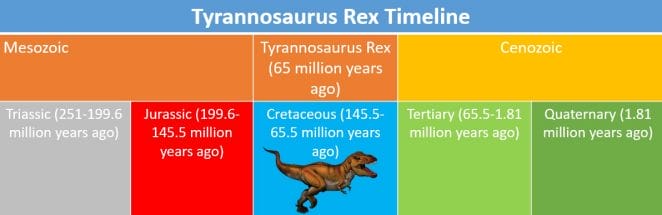
The relative placements of fossils in the ground are one method of dating them. Paleontologists are, in effect, peering back in time when they dig deeper into sedimentary rock. Because older layers are buried when sediments transported by wind and water accumulate, the bottom layers in a geological sequence are normally the oldest and the top layers the youngest. Scientists can use the quantity of specific radioactive elements—often radiocarbon or potassium—present in rocks and fossils to estimate when a rock was produced or when an animal died.
9: How many eggs did Tyrannosaurus lay?
Although no T. rex eggs or nests have ever been discovered, other Tyrannosaur relatives’ remains imply that they deposited elongated eggs in batches of 20 or more.

Adult T. rexes may have guarded their nests and fed their young in the same way that birds and crocodile parents do (their closest modern relatives), but there is no concrete evidence of prenatal care.
10: How long did Tyrannosaurus rex live?
Tyrannosaurus rex lived for approximately 28 years. Previous research revealed it went through a growth surge in its adolescence, but scientists didn’t know much about how it evolved from a hatchling to a powerful predator until recently.

In January 2020, researchers discovered that the bones of Nanotyrannus—a smaller tyrannosaur thought to have lived alongside T. rex—were more likely from a young T. rex than from another species. The study suggests that Tyrannosaurus rex’s growth rate fluctuated as it grew older, and that it could slow down its growth when food was scarce, which would be a significant evolutionary benefit.
11: How old is the oldest Tyrannosaurus rex?
The T. rex grew rapidly, reaching adult size as a teenager, and died young, according to growth rings. The oldest specimen that was examined was only 28 years old. Animal bones, like tree trunks, can generate growth rings over time. The number of rings on a specimen indicates its age, while the breadth indicates whether it was still expanding. However, only a few bones have a complete set of growth rings; sadly, the massive limb bones that are best preserved as fossils are not among them.
12: The original name for tyrannosaurus rex was “Manospondylus.”
The first T. rex specimen was discovered by renowned palaeontologist Edward Drinker Cope in 1892, and Cope briefly pondered renaming his discovery Manospondylus gigax, which is Greek for “giant thin vertebrae.” It was up to Henry Fairfield Osborn, the then-president of the American Museum of Natural History, to erect the iconic name Tyrannosaurus rex, the “tyrant lizard king,” following additional stunning fossil discoveries.
13: Other interesting Tyrannosaurus Rex facts:
- Tyrannosaurus is a Greek term that means “tyrant lizard.”
- T. rex Sue was auctioned for US$8.3 million in October 1997, the highest price ever paid for a dinosaur fossil until T. rex Stan was auctioned for US$31.8 million on October 7, 2020.

Quiz: T. REX Quiz: How well do you know T. REX?
Sources:Wikipedia, American Museum of Natural History





GIPHY App Key not set. Please check settings