Tyrannosaurus rex was one of the world’s most massive and terrifying animals. Despite the fact that Tyrannosaurus rex is a well-known dinosaur, palaeontologists have only found a few complete specimens. The legendary Barnum Brown, a curator at the American Museum of Natural History, unearthed the first T. rex fossil, and the Museum now houses one of the rare T. rex specimens on display.
Test your knowledge on Tyrannosaurus rex, the greatest predator, by taking this 10-question quiz.
Each question has a time limit of 30 seconds. The quicker you respond, the greater your score. When you’re finished, attempt to beat your previous best score!
#1. What’s the difference between the terms “Tyrannosaurus rex” and “tyrannosaur”?
“Tyrannosaurs” is the name of a group of closely related dinosaurs. This group includes dozens of different kinds of animals, and its biggest and most famous member is Tyrannosaurus rex. Fossils show that tyrannosaurs evolved for over 100 million years, with T. rex appearing during the last two million. Tyrannosaurs lived between about 167 and 66 million years ago. T. rex lived between about 68 and 66 million years ago.
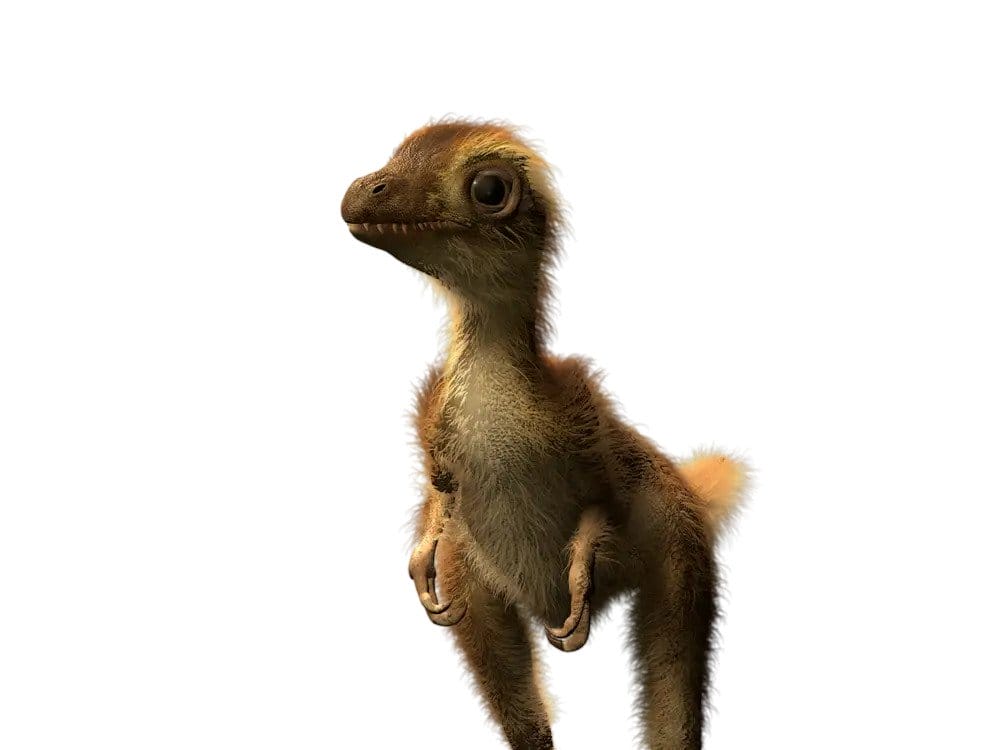

#2. Every fearsome T. rex was once a helpless chick. How big was a newly hatched T. rex?
A baby T. rex had very different features than an adult T. rex. It hunted and survived differently too! Its bladelike teeth and light skull were better suited for snatching small prey than for crushing large bones. Its slim, lightweight body and long legs made it quick and agile—useful for avoiding predators.
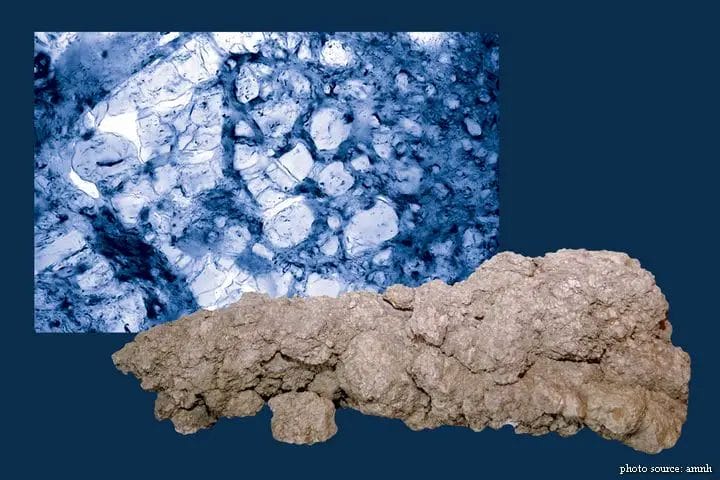

#3. Paleontologists use high-tech tools to study coprolites, or fossilized poop. What meal leftovers can be seen in this CT scan of a T. rex coprolite?
Scientists long suspected T. rex could crunch through bones, thanks to its powerful skull and teeth. Now there’s proof in its poop! In fact, crushed bone makes up 30 to 50 percent of this fossil.
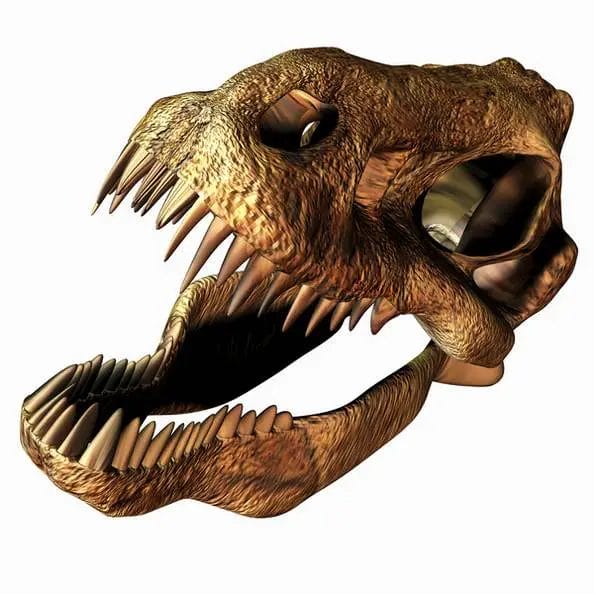

#4. How did T. rex's teeth contribute to its efficiency as a predator?
A T. rex bite was powerful enough to crush bone. It could bite with about 34,000 newtons of force, like being crushed under the weight of three cars. No known animal, extinct or alive, can bite with such force.
#5. A juvenile T. rex looks very different from an adult. Which of these is a 12-year-old T. rex?
A juvenile T. rex had more traits in common with adult members of smaller tyrannosaur species than with its own parents. They all had lighter skulls, long legs, and sharp teeth that could tear flesh. Feathers covered most of their bodies, probably for insulation, camouflage, species recognition, or display.
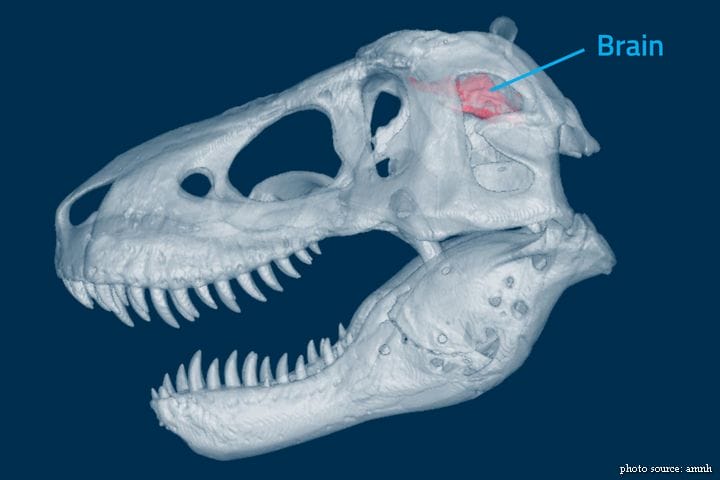
#6. Fossilized skulls can help scientists determine the precise shape and size of a dinosaur’s brain. What does this brain cast of a T. rex tell us about the animal’s senses?
By comparing brain casts of T. rex to the brains of its closest living relatives—birds and crocodilians—scientists can tell that T. rex had excellent vision, hearing, and sense of smell. Other features, like forward-facing eyes, which were the size of oranges, gave this predator superior depth perception and helped it see far into the distance.
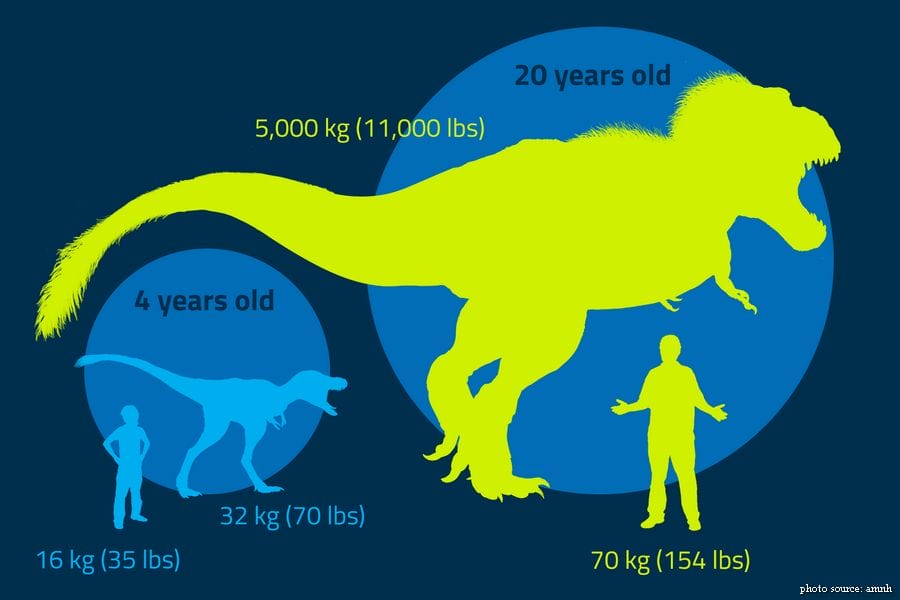
#7. A 4-year-old T. rex is twice as heavy as a 4-year-old human. A 20-year-old T. rex is how many times heaver than a 20-year-old human?
T. rex grew much bigger and much faster than humans, gaining up to 2.1 kilograms (4.6 pounds) in just one day! T. rex juveniles were much smaller and weaker than their parents. But they were quick and nimble, enabling them catch smaller, faster prey. Juveniles and adults had different diets and probably lived in different habitats.
#8. A palaeontologist from the American Museum of Natural History discovered a new dinosaur species, Tyrannosaurus rex, more than a century ago. Who discovered the fossil, and where was it discovered?

Barnum Brown described excavating the T. rex fossils as “hot dirty work with the thermometer ranging up to 110° Fahrenheit without any shade.” He and his team found a total of three T. rex individuals in the early 1900s, including two nearly complete skeletons!

#9. What color was T. rex?
By studying tyrannosaur fossils, scientists think that T. rex was probably covered with scales and feathers. So T. rex could have been as colorful or as drab as its living relatives, like the birds and lizards shown here!

#10. What does the name “Tyrannosaurus rex” mean?
Tyrannosaurus rex was the top predator in its ecosystem. With its huge size, sharp claws, and bone-crushing bite, it dominated the competition. No wonder its name means the tyrant lizard king!








