Maiasaura was a duck-billed dinosaur that lived in late Cretaceous North America around 80 million years ago. Maiasaura were herbivores, meaning they preferred plants to meat. They walked on all fours, but could also feed by standing on two legs.

Long, rigid tails let Maiasaura maintain their balance. Because their lips resemble a duck’s bill, Maiasaura are known as duckbill dinosaurs. A duckbill dinosaur is known as a hadrosaur. Find out more interesting Maiasaura facts.
1: Maiasaura quick facts:
Name: Maiasaura (Greek for “good mother lizard”); pronounced my-ah-SORE-ah
When it lived: Late Cretaceous, 80-75 million years ago
Type of dinosaur: Ornithopod
Location: USA
Habitat: Inland forests and woodlands.
Length/Weight: 9 meters/2500kg
Diet: Herbivorous
Distinguishing Characteristics: They have a small spiked crest between their eyes, a thick nose, and a flat beak.
Named by: Horner and Makela (1979)
2: What does the name Maiasaura mean?
In Greek, “Maia” refers to a goddess and means “good mother,” while “saura” is the female equivalent of “saurus,” which means lizard or reptile.
3: How do you pronounce ‘Maiasaura’?
The name Maiasaura is pronounced in a manner that is similar to “my-ah-SORE-ah.”
4: Why is Maiasaura called the good mother lizard?
It was given the name Maiasaura after the nests discovered in western Montana’s Two Medicine Formation, also known as Egg Mountain. Several Maiasaura babies have already born from these nests. The Maiasaura was discovered to be a dinosaur that looked after its offspring, earning it the nickname “good mother lizard.”
5: What did Maiasaura eat?
Maiasaura was a herbivore, which meant it ate plant matter like leaves, seeds, woody plants, tree bark, ferns, branches, rotten wood and berries.
Given its size, palaeontologists estimate that an adult hadrosaur would need to consume roughly 200 pounds of plants every day. The Maiasaura, on the other hand, would have to feed its hatchlings, therefore fully fledged Maisaura would have been continually trimming plants. Duck-billed Maiasaura peeblesorum used to graze on four legs when looking for food.
6: Who discovered Maiasaura?
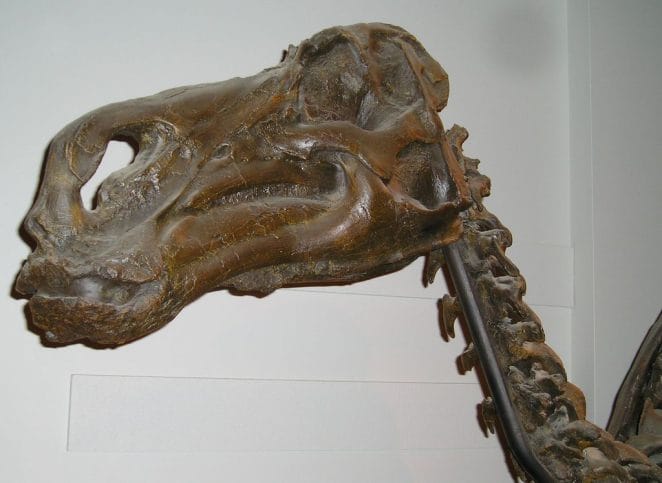

Laurie Trexler discovered the first Maiasaura fossils in 1978, although they were not named until 1979. It was later described by Jack Horner and Robert Makela, who worked as the paleontologic advisor for the Jurassic Park films.
7: When was the Maiasaura first discovered?
In 1978, a team of American scientists led by palaeontologist Jack Horner discovered the first Maiasaura fossils in the Badlands of western Montana. The researchers discovered a number of nests, eggs, baby Maiasaura, juveniles, and adult animals at the site they discovered.
8: Where was Maiasaura found?
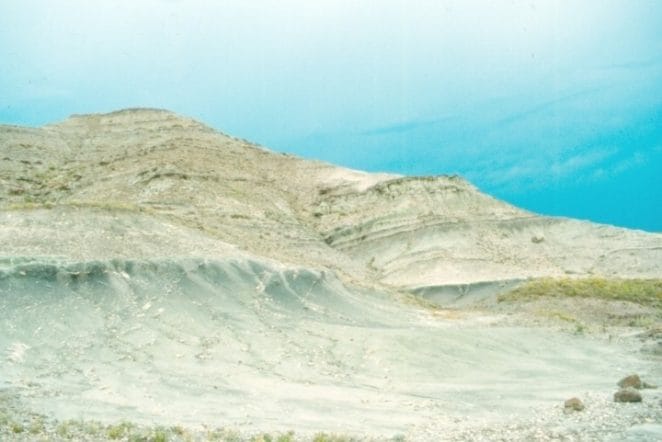

In 1978, a Maiasaura nesting site was discovered in Choteau, Montana, in the Two Medicine Formation. The remains of an adult Maiasaura were discovered near a nest of juvenile dinosaurs, each measuring around 1 metre (3.3 feet) in length. Around 200 individual fossils have been discovered, offering evidence of dinosaur nesting behaviour.
9: When was the Maiasaura alive?
Maiasaura existed during the late Cretaceous, between 80 and 65 million years ago, near the conclusion of the Mesozoic. They were migratory land creatures who preferred the lush greenery of what is now Montana.
10: What kind of climate did Maiasaura inhabit?
Maiasaura lived in inland forests and woodlands, according to evidence collected at the site where the dinosaurs’ bones were discovered. Given that they roamed in vast herds and need enough of foliage to graze on, the projected Maiasaura environment would have been ideal for them.
11: What was Maiasaura’s height and weight?
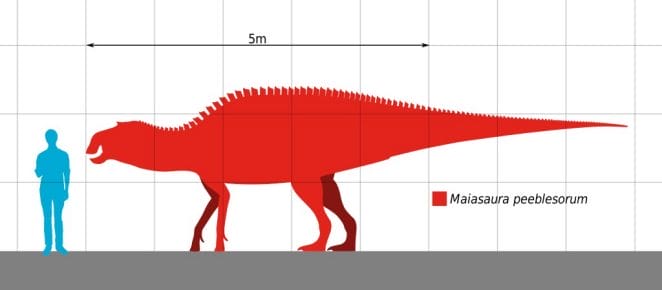
Maiasaura measured 9 metres (29.5ft) in length, 3 metres (10ft) at the hips, and weighed 2.5 tonnes (2500kg).
12: How many eggs did Maiasaura lay?
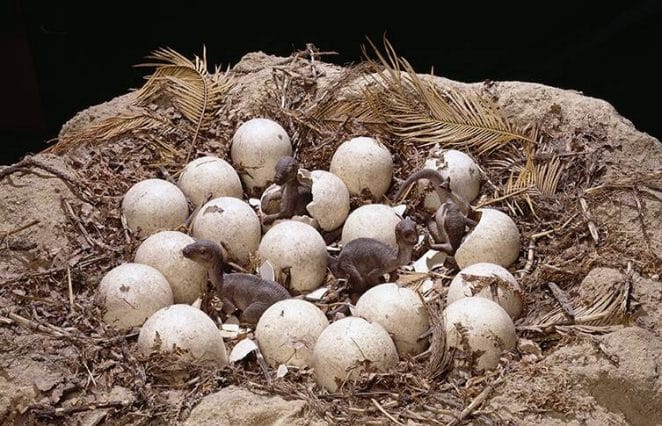

Maiasaura is best known for its parenting activity, which began with females who laid up to 30 or 40 eggs at a time in well built nests. Due to the fact that female Maiasaura laid and incubated so many eggs, the eggs of this dinosaur were very small by Mesozoic standards, roughly the size of current ostrich eggs.
13: What was Maiasaura known for?
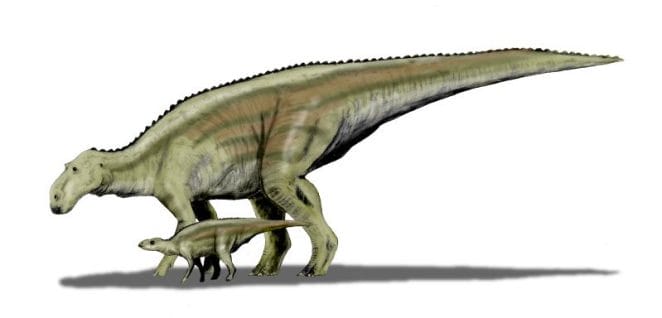
Maiasaura is known for its parenting skills. Its skeletal remains indicate that the adults lived in herds and cared for their young in huge nesting areas. These Late Cretaceous dinosaurs are likely to have nested in vast colonies and lived between 80 and 75 million years ago. The parents may have provided their hatchlings with substantial food and protection.
14: What dinosaurs did Maiasaura live with?
Before the Cretaceous-Tertiary extinction 65 million years ago, it was one of the last dinosaur species to change. Velociraptor, Albertosaurus, and Troodon were carnivores that probably ate Maiasauras. Other dinosaurs that lived at the same time as Maiasaura were Ankylosaurus, Parasaurolophus, Corythosaurus, and Dryptosaurus.
15: How did the Maiasaura protect itself?
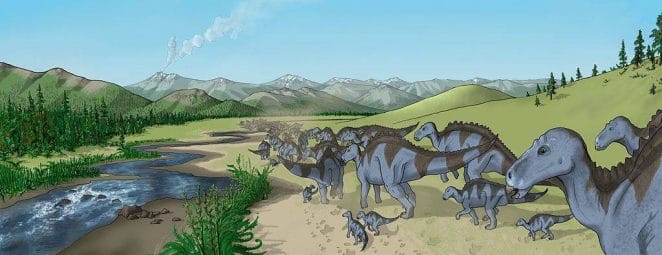
Maiasaura peeblesorum’s large, muscular tail was its only defence against predators. Maiasaura migrated, which meant they moved around in search of food at different times of the year. They moved in herds of 10,000 or more. They were safer from predators by moving in such a large herd.
16: How did Maiasaura move?
Maiasaura, according to palaeontologists, alternated between bipedal and quadrupedal mobility. They were bipedal, or walked on two legs, as juvenile. When they reached adulthood, they normally moved around on all four legs, though they retained the ability to do both. It would have grazed using its front limbs because its hind legs were bigger and stronger and utilised to run.
17: How many teeth does a Maiasaura have?
Maiasaura was equipped with a toothless beak for snipping plants and hundreds of teeth for chewing and grinding. Although all of the chewing had worn down its teeth, replacing them was not an issue.
Each tooth had four or five replacement teeth sprouting in its place. Maiasaura required its teeth in order to continue eating. It had to eat regularly in order to keep its weight stable. To stay alive, it had to eat a lot of leaves, berries, seeds, and woody plants every day.
18: How fast can Maiasaura run?
Maiasaura, like other hadrosaurs, was most likely a fast runner, which served as its primary protection against predators. According to scientists, hadrosaurs like Maisaura could reach speeds of up to 28 mph.
19: Why is the finding of Maiasaura significant?
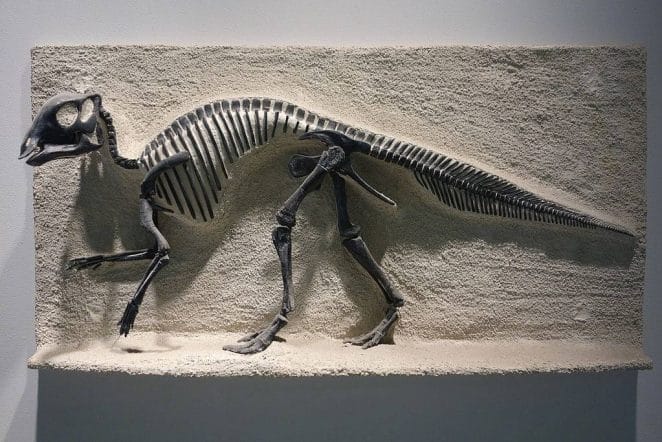

The late 1970s discovery of Maiasaura offered the first evidence for parental care in dinosaurs. Thousands of Maiasaura bones were unearthed in northern Montana. Maisaura is known from the remains of eggs, babies, juveniles, and adults. Maiasaura’s finding was significant because it demonstrated for the first time that giant dinosaurs cared for and nurtured their offspring.
20: What was the Maiasaura predators?
The most likely predators of Maiasaura peeblesorum were Albertosaurus and Troodon. Maiasaura peeblesorum lived with Ankylosaurus and Dryptosaurus, while Parasaurolophus and Corythosaurus were duck-billed dinosaurs that lived alongside Maiasaura peeblesorum.
21: Other interesting Maiasaura facts:
- The hadrosaur Maiasaura peeblesorum was the first dinosaur to travel into space. Astronaut Loren Acton transported bone and eggshell from a nesting site to SpaceLab 2 in 1985.
- In 1985, Maiasaura was designated as Montana’s state dinosaur.
- Maiasaura holds the distinction of being the first dinosaur to be discovered with its offspring. This was the first biological proof that these massive reptiles feed and raise their offspring.





GIPHY App Key not set. Please check settings