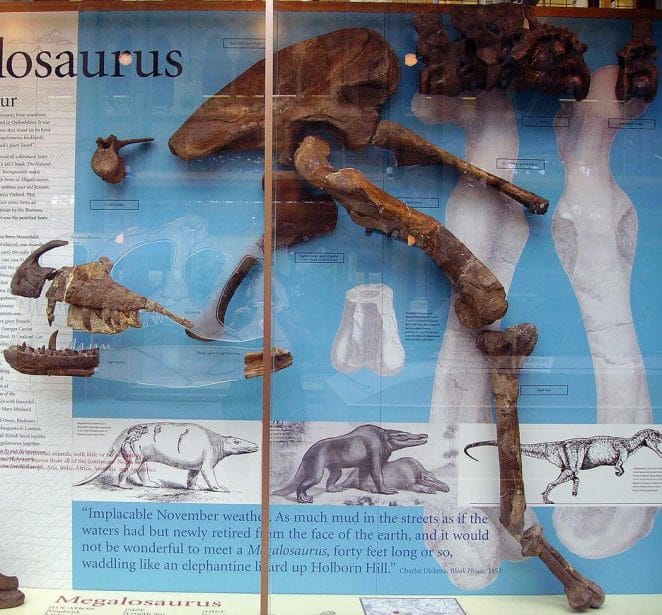
Megalosaurus was a big meat-eating dinosaur that lived somewhere between 170-155 million years ago. In 1676, the first dinosaur fossil unearthed in England was Megalosaurus. Megalosaurus’ teeth and bones were the first dinosaur fossils to be named in 1824 by William Buckland.

Let’s find out more interesting facts about Megalosaurus.
1: Megalosaurus quick facts:
Name: Megalosaurus (Greek for “great lizard”); pronounced MEG-ah-low-sore-us
When it lived: Mid Jurassic, 170-155 million years ago
Type of dinosaur: Large Theropod
Location: United Kingdom, Portugal, France
Habitat: Tropical, tall, and densely forested terrestrial environments.
Length/Weight: 6 meters/700kg
Diet: Carnivorous
Distinguishing Characteristics: A robust neck, strong limbs with claws, sharp, conical teeth, a strong jaw, a large tail, and a large head.
Named by: Gideon Mantell (1827)
2: What Did Megalosaurus Look Like?
The Megalosaurus was a bipedal Theropod, meaning it walked on both of its hind legs. Megalosaurus had a long, thick neck and a large head. Megalosaurus’ jaws were powerful, with curved, pointed, and dagger-like teeth. The Megalosaurus’ front legs or arms were short yet powerful.
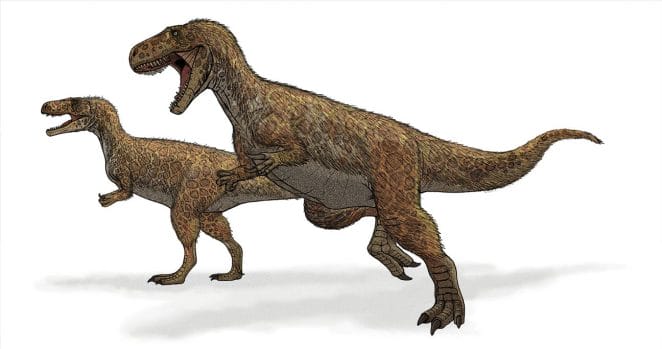
The front legs had grabbing, clawed digits that functioned as hands. Both feet had three claws on each toe. This tail countered the horizontal tilt of the torso. The preserved Megalosaurus skeleton is highly ossified, suggesting that the animal was robust and muscular. The physique as a whole was hefty, as were the bones.
3: What does the name Megalosaurus mean?
Megalosaurus is a combination of two Greek words: ‘megas’ and ‘sauros.’ Megas means ‘large, enormous, or tall,’ while sauros means ‘lizard.’ Megalosaurus translates to ‘great lizard.’
4: How do you pronounce ‘Megalosaurus’?
The name Megalosaurus is pronounced ‘MEG-ah-low-sore-us.’
5: What did Megalosaurus eat?
The Megalosaurus was a bipedal top predator and carnivore that preyed on Sauropods and Stegosaurs, as well as insects, reptiles, and early mammals.
6: Who discovered Megalosaurus?
William Buckland, a palaeontologist, determined in the early 1820s that the bones belonged to gigantic reptiles. In a geological study of southeast England published in 1827, Gideon Mantell wrote about Megalosaurus and named the species Megalosaurus bucklandii after William Buckland.
7: When was the Megalosaurus first discovered?
The first Megalosaurus specimen was discovered in 1676 in Oxfordshire, England, in the Taynton Limestone Formation. Biologists at the time were baffled by the fact that it was merely a bone fragment.
8: Where did Megalosaurus live?
Megalosaurus lived in Europe during the Jurassic period. Its fossils have been discovered in Portugal, the United Kingdom, and France, among other places.
9: When was the Megalosaurus alive?
Megalosaurus dinosaurs lived approximately 170-155 million years ago, during the Bathonian epoch of the Middle Jurassic period.
10: What kind of climate did Megalosaurus inhabit?
Megalosaurus flourished in tropical and lush terrestrial settings during the Middle Jurassic period, allowing them to hunt and fight prey such as Sauropods, Stegosaurs, and early mammals. Tall trees, such as enormous sequoias and pines, would have thrived in these locations. Tree ferns, palm trees, ginkgoes, and horsetails, for example, would have grown as well.
11: What was Megalosaurus’s height and weight?
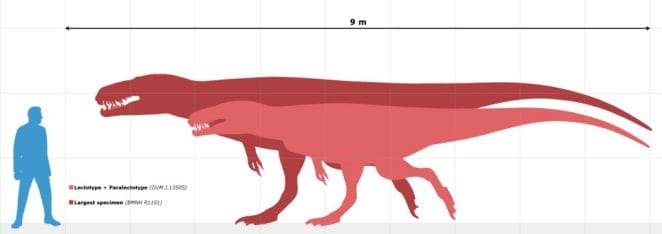
Megalosaurus was a typical theropod dinosaur with short arms and a long tail that stood on two legs. It was around 6 metres (20 feet) long and weighed about 700 kilos (1,500 lb).
12: Is the Megalosaurus bigger than a T Rex?
The Tyrannosaurus rex was larger than the Megalosaurus. The Tyrannosaurus rex was 40–42 feet (12.2-12.8 metres) long, while the Megalosaurus was just 20 feet (6 metres) long. In addition, the T. rex weighed 8,800 kg compared to 700 kg for the Megalosaurus.
13: How many teeth does a Megalosaurus have?
Megalosaurus had 13 teeth on its maxilla, all of which were quite big. The crown was around 2.8 inches long (7 cm). The Megalosaurus had roughly 30-32 teeth in total.
14: How fast can Megalosaurus run?
Megalosaurus, as a carnivorous bipedal Theropod, might have travelled at speeds of up to 27 mph (43.4 kph).
15: Why is the finding of Megalosaurus significant?

Megalosaurus was the first non-avian dinosaur to be documented in scientific and paleontological journal literature. Megalosaurus was the dinosaur that started a great many things, including the science of palaeontology, the debate about whether dinosaurs should be called names that end in “saurus” even though they are not “lizards,” and a lifetime of interest in the animals that walked the Earth before we did.
16: Other interesting Megalosaurus facts:
- Megalosaurus bucklandii is a Middle Jurassic dinosaur that was originally described in 1827, making it one of the first dinosaurs ever discovered. When Richard Owen originally described the Megalosaurus, it sparked people’s curiosity in dinosaurs.
- Richard Owen utilised the carnivorous Megalosaurus, herbivorous Iguanodon, and armoured Hylaeosaurus as the three genera to create Dinosauria.
- A lower femur from the Taynton Limestone deposit was the first Megalosaurus fossil discovered.
Sources:Wikipedia





GIPHY App Key not set. Please check settings